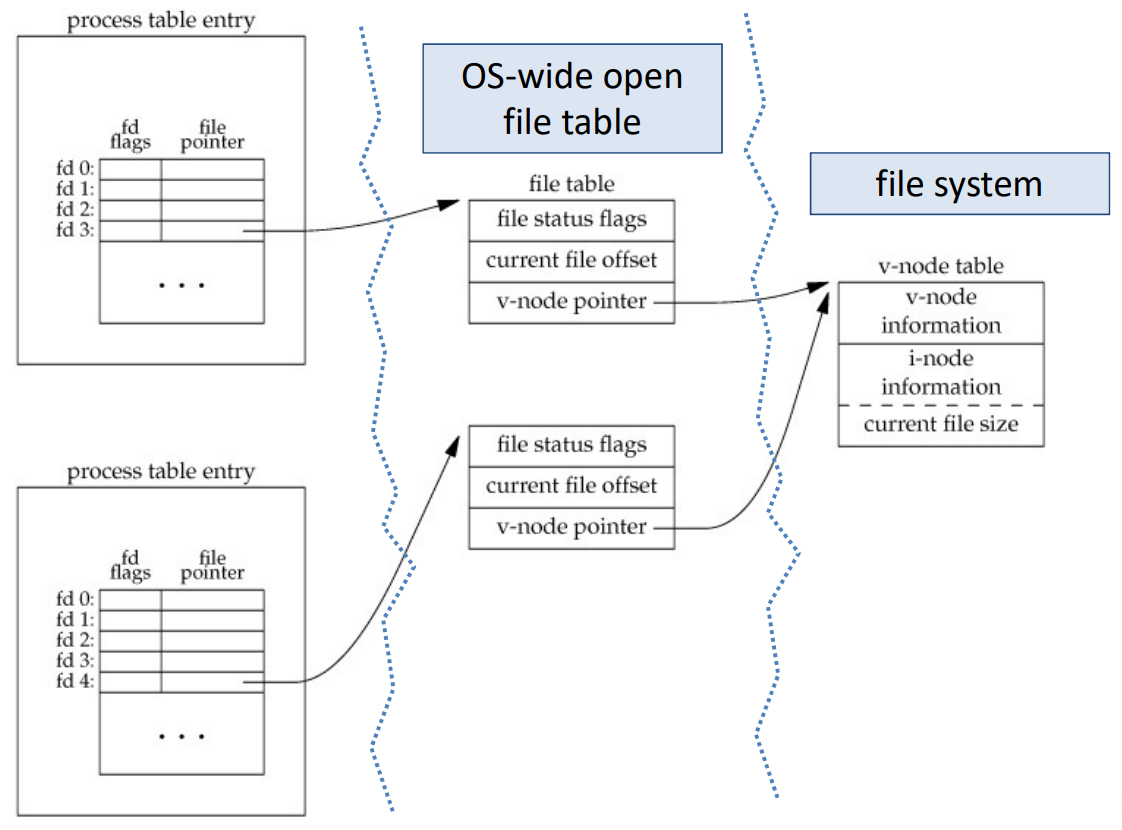
두 개의 processes에서 각각 file에 대한 연산을 할 때 자신의 file descritor가 관린한다.
OS level에서는 global하게 file table을 관리한다. 어떤 file의 descriptoy가 생성되었는지 등
각 processes는 해당되는 file에 대한 descriptor로 접근하고 실제 file system에서는 i-node를 매체로 data를 조작한다.
v-node 객체 ??
#include <unistd.h>
int dup(int fd);| 동일한 file에 대해서 중복된 file descriptor를 만들수 있다. |
| fd : file descriptor |
| return 중복되어 접근할 수 있는 새로운 descriptor / -1 |
#include <unistd.h>
int dup2(int fd1, int fd2);|
기존의 file descriptor를 복제될 file descriptoy 지정 dup(..)와 동일한 기능을 한다. 새로운 것을 원하는 걸로 만든는 것 |
|
fd1 : source file descriptor fd2 : destination file descriptor |
|
return 복사된 새 file descriptor(fd2) / -1 |
fileno ,descriptor 반환
Link
연관을 시키는 참조하는 것이다.
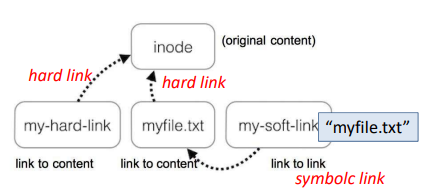
- Symbolic link (sofr link)
- 원본 file이 존재하는 상황에서 link를 만들어진다.
- file의 이름에 link한다.
- target file의 path가 기록된 file
- target file이 지워지면 접근할 수 없다.
- $ ln -s origianl_file symbolic_link_name
- Hard link
- target file의 i-node를 직접 가르킨다.
- 실제 file system의 정보는 가진다.
- target file이 update 되면 같이 update
- target file이 지워져도 i-node가 남아있어서 접근할 수 있다.
- $ ln original_file hard_link_name
shell command에서 실행할 수 있다.
ln : link file 생성
권한의 앞에 l이 붙으면 sysmbolic link
#include <unistd.h>
int link(const char *existing, const char *new_link);| existing에 대한 new_link라는 hard link file 생성 |
|
existing : 원래 이름 new_link : 생성할 hard link의 이름 |
#include <unistd.h>
int symlink(const char *existing, const char *link_name);| existing에 대한 link_name 라는 symbolic link 생성 |
|
existing : 원래 이름 link_name : 생성할 symbolic link의 이름 |
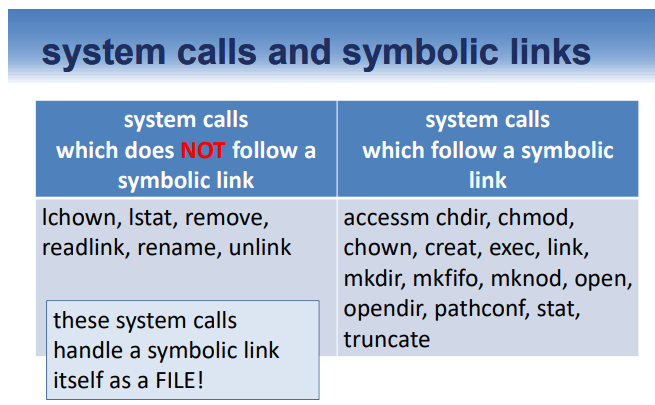
symbolic link를 따르는, 따라서 적용되는 system call
#include <unistd.h>
int readlink(const char *path, void *buf, size_t bufsize);| 해당 link하고 있는 원본 파일을 알아내는 함수 |
|
path : link 이름 buf : 정보를 담아올 buffer bufsize : buffer 크기 |
| return read한 byte 수 / -1 |
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);| 어떤 파일에 대한 정보를 가지고 있는 |
|
path : file의 이름 buf : 정보를 반환 받는 stat이라는 구조체의 주소 |
| return 0 / -1 |
int lstat(const char *path, struct stat *buf); |
어떤 파일에 대한 정보를 가지고 있는 symbolic link일 경우 link file에 대한 정보를 가져온다 |
|
path : file의 이름 buf : 정보를 반환 받는 stat이라는 구조체의 주소 |
| return 0 / -1 |
int fstat(int fd, struct stat *buf);| file descriptor를 이용해서 정보를 얻어오는 함수 |
|
fd : file descriptor buf : 정보를 반환 받는 stat이라는 구조체의 주소 |
| return 0 / -1 |
struct stat
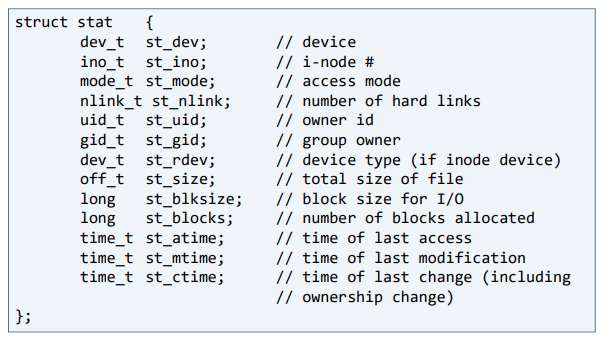
- device id
- i-node 번호
- 접근 권한
- hard link 수
- user id
- group id
- device type
- 전체 크기
- block 수
- 마지막 접근(+read) 시간
- 마지막 변경(+data 수정) 시간
- 마지막 수정(+file 정보) 시간
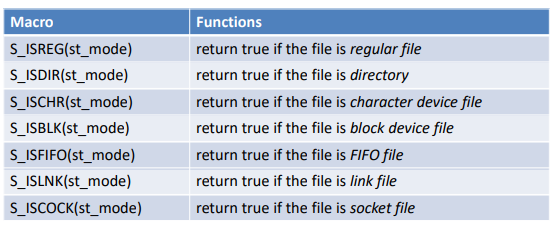
어떤 특징이 있는지 알 수 있는 Macro 함수 자주 쓰는거 만들어놨다. 위에꺼는 file type에 대한 것이다.
'시스템 프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 시스템 프로그래밍 4장 - Concurrent Process (0) | 2020.05.05 |
|---|---|
| 시스템 프로그래밍 3장 - System call : File I/O Permission, ID (0) | 2020.05.05 |
| 시스템 프로그래밍 3장 - System call (0) | 2020.05.05 |
| 시스템 프로그래밍 2장 - Library call : File I/O function (0) | 2020.05.05 |
| 시스템 프로그래밍 2장 - Library call : File I/O (0) | 2020.05.05 |