프로세스를 생성하는 것은 굉장히 system overhead가 드는 작업이다.
- process는 독립적으로 동작하는 큰 단위이다.
process에 포함된 것들
- address space ( code, data, stack, heap, ...)
- OS resource(open file descriptor, account, env, ...)
- process에 현재 실행하는 hardware 상태( PC, SP, registers, ...)- process간 data통신을 하기 위해서는 OS의 resource를 거쳐서 작업한다.
*process를 생성해서 실행해도 변하지 않고 사용할 수 있는 resource들이 있다.
- code, data
- privilege상태
- OS의 resource들 (file descriptor, socket, ...)
*반면에 process가 실행되면서 실시간으로 변하는 값도 있다.
- CPU의 상태(register, SP, stack, ...)
여러개의 작업을 동시에 작업하기 위해서 어떻게 작업할 수 있는가?
공유할 수 있는 건 공유하고, 별도로 작동하는 것만 별도로 운영한다! -> Thread
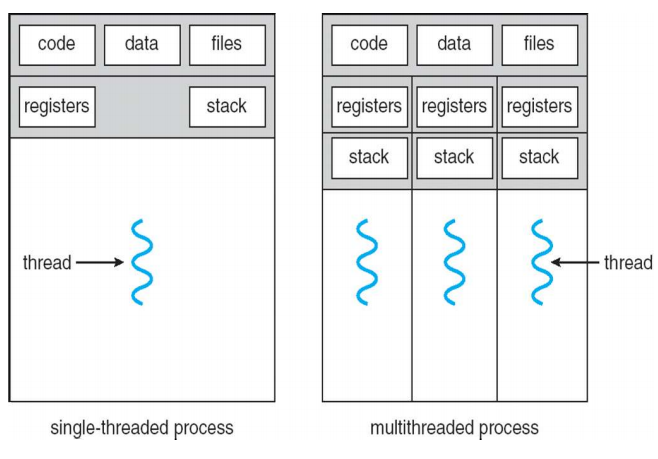
Thread란?
Prcocess 내부에서 독립적인 제어 흐름을 가지는 단위
하나의 process는 자신이 수행되는 program의 흐름 상태(PC, stack, register)를 가진다.
이런것들을 다른 process가 아닌 하나의 process내에서 여러 개 가지는 것이! - > multi Thread
thread는 CPU의 scheduling 단위이다.
multi Thread는 process내에서 여러 개의 제어 흐름을 가진다.
Thread의 구성
thread ID, PC, register, stack값들을 관리할 수 있는 stack영역
code, data OS resoure는 multi-thread에서 공유된다.
z.B.)
- web browser
- a thread which display images and text
- another thread which receives data from network
- word processor
- a thread which draws a graph
- second thread which reads key or mouse events by user
- third thread which check spelling and grammar
- Web server case
- single-threaded server
- requests from users are handled sequentially by one process
- multi-process server
- a new process is created for a new client
- high process overhead
- multi-threaded server
- almost same as the multi-process server, but the overhead is quite small
- single-threaded server
대부분은 OS Multi Thread safe library를 제공한다.
- Linux/Unix
- POSIX Pthreads
- Mach C-threads, Solaris Threads
POSIX는 standard API(IEEE 1003.1c)를 정의한 것이다.
thread에 대한 creation, management, synchronization 등에 대해서 표준으로 재정해놓은것
thread가 어떻게 행동해야되는가에 대해서 단지 스펙만 정리했다.
이것은 OS마다 어떻게 정의하는가에 따라 달라질 수 있지만 user level에서 동일하게 표준화 되어있다.
Linux계열의 OS에서는 thread를 Posix stand에 맞게 구현되어있다.
pthreads libraray
- <pthread.h>에 존재한다.
- libpthread.a라는 library형태로 구현되어있다.
- 이것은 일반적인 gcc에 포함되어있지 않기 때문에 일반적인 gcc에서 compile안된다.
그래서 compile option : -lpthread 를 같이 입력해야한다.
$ gcc test.c -lpthread
Pthreads API and data types
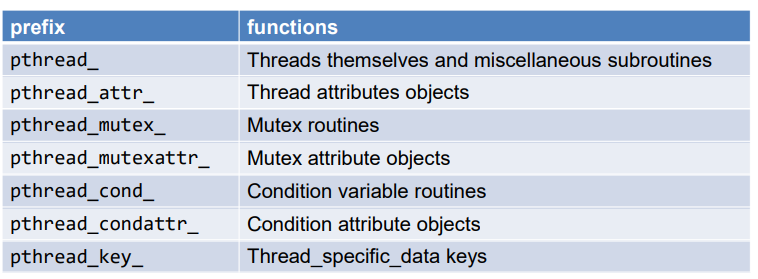
일반적인api system call 함수들은 pthread_로 시작한다.
이런 data type, 함수들을 이용해서 프로그램한다.
pthread_create
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_create( pthread_t *thread,
pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start_routine)(void *),
void *arg);| thread를 생성하는 thread API |
|
thread : OS에서 할당된 thread id를 받을 포인터 attr : 생성된 새로운 thread에 대한 attribute를 받을 포인터 // 사용하지 않으면 null로 넘겨줘도 된다. start_routine : 함수 포인터 thread가 생성될 때 thread가 생성될 때 thread가 실행해주는 작업을 함수로 정의한 것 arg : 이 함수에 전달해줄 argument를 포인터 형태 전달 int, data struct |
| return 0 / error number |
기본적으로 process는 main thread를 가진다.
추가적으로 만들기 위해서 이것을 사용한다.
thread가 만들어지면 독립적으로 동작을 한다.
현재 process에서 너무 많은 tread를 만드는 것을 방지하기 위해서 maximum이 제한되어져 있다.
Terminating a pthread
-직접
- 아무것도 부르지 않더라도 전달한 함수가 종료되면 thread가 종료된다.
- pthread exit를 불러서 종료할 수 있다.- 다른 thread에서
- pthread id를 이용해서pthread\_cancel을 불러서 종료된다.
- process자체가 종료되면 관련된 thread들도 종료된다.void pthread_exit(void *retval)|
특정 thread에서 자신의 thread를 종료하는 방법 이것을 함수를 이용해서 종료하는 것을 권장한다. - main thread에서 실행하면 main은 종료되고 다른 thread는 계속 실행된다. - main thread에서 exit를 호출하면 process가 종료되기 때문에 모든 thread 종료 open file을 close하지 않고 process가 종료될때 같이 종료된다. |
| retval : 이 값을 해당 pthread_joind으로 종료되기를 기다리는 다른 thread에게 전달한다. |
| return |
Detaching / Joining a thread
thread가 생성될 때 joinable or detached 속성을 가진다. default는 joinable이다.
- detached thread
- pthread_detach함수를 이용해서 분리한다.
- 분리된 thread는 결코 join될 수 없이 독립적으로 관리된다.
- 만약에 detach된 thread가 종료가 될 경우 resource는 즉시 반환된다.
- joinable thread
- 다른 thread와 join되어있다.
- thread가 사용하던 자원들은 반환되지 않고 join된 thread에게 넘겨준다.
int pthread_join(pthread_t tid, void **retval); |
어떤 thread가 다른 thread에게 join될 때까지 기다리는 함수 join된 thread가 arg를 넘겨줄 때까지 pthread_join은 block된다. pthread_exit로 종료가 되면 pthread_join으로 thread가 join되고, retval에 넘겨받는 값을 받는다. |
|
tid : join을 기다리는 thread의 id retval : join된 thread가 넘겨주는 parameter를 받는 변수 poiter |
| return 0 / error number |
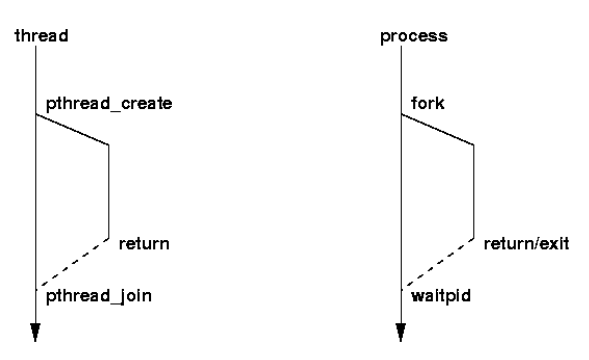
process vs thread 생성과 종료
int pthread_self(void);
| thread id를 가져올 수 있다. 자기자신의 id |
| return 호출된 thread id |
int pthread_equal(pthread_t t1, pthread_t t2);| 특정 두 thread가 동일한 thread인지 확인 |
|
t1 : thread 1 t2 : thread2 |
| return 같을경우 nonzero / 다를경우 0 |
'시스템 프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 시스템 프로그래밍 6장 - Thread : Synchronization (0) | 2020.05.06 |
|---|---|
| 시스템 프로그래밍 6장 - Thread : Cancellation (0) | 2020.05.06 |
| 시스템 프로그래밍 5장 - Process Control : Daemon (0) | 2020.05.05 |
| 시스템 프로그래밍 5장 - Process Control : Process Start & Exit (0) | 2020.05.05 |
| 시스템 프로그래밍 5장 - Process Control : PID (0) | 2020.05.05 |